Upgrading Computer Components - The Complete In-Depth Guide
So you want to upgrade your computer but have no clue where to start? There are some things to look at before deciding upon an answer. Most people would rather upgrade then build there own computer, now this article will explain how to do this.
Notes To Know:
Bottleneck: This refers to when a computer component slows down the rest of the computer either due to being outdated or just simply slow.
Processor: The processor is the central processing unit (CPU) is probably the single most important component in your system. This controls the way your computer acts and thinks along with calculating data. It is pretty much the "brain" of your computer.
Component Upgrade List:
Not everyone can afford the latest processors and technology at any given time
so this will help you solve the bottle-necking going on in your computer
while giving you a good system for the next couple of years. Whether you are a gamer, a everyday user, or a enthusiast that love to push your computer to the edge this guide will have something in here for you. These are some examples of what bottle-necking really is and how to spot it in your system.
For Example:
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU: AMD Athlon II X2 370K 4.2GHz Dual-Core Processor ($49.99 @ Amazon)
Motherboard: ASRock FM2A85X Extreme4 ATX FM2 Motherboard ($79.99 @ Newegg)
Memory: G.Skill Ripjaws X Series 8GB (2 x 4GB) DDR3-1866 Memory ($74.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Kingston SSDNow V300 Series 120GB 2.5" Solid State Disk ($84.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Seagate Barracuda 1TB 3.5" 7200RPM Internal Hard Drive ($59.97 @ SuperBiiz)
Video Card: PowerColor Radeon HD 7990 6GB Video Card ($644.98 @ Newegg)
Case: NZXT Switch 810 (Black) ATX Full Tower Case ($136.00 @ Amazon)
Power Supply: XFX 750W 80 PLUS Bronze Certified ATX12V / EPS12V Power Supply ($97.99 @ Amazon)
Optical Drive: Lite-On iHAS124-04 DVD/CD Writer ($17.98 @ Outlet PC)
Operating System: Microsoft Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 (OEM) (64-bit) ($89.00 @ Amazon)
Total: $1335.88
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-10 01:28 EDT-0400)
Note: The bottleneck in this system would be the processor since it is a dual-core most systems at this level require at least a quad-core. So if I was to switch it to one of these two options:
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU: AMD Phenom II X4 980 Black 3.7GHz Quad-Core Processor ($109.99 @ SuperBiiz)
Motherboard: Asus M5A97 LE R2.0 ATX AM3+ Motherboard ($84.24 @ Amazon)
Memory: G.Skill Ripjaws X Series 8GB (2 x 4GB) DDR3-1866 Memory ($74.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Kingston SSDNow V300 Series 120GB 2.5" Solid State Disk ($84.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Seagate Barracuda 1TB 3.5" 7200RPM Internal Hard Drive ($59.97 @ SuperBiiz)
Video Card: PowerColor Radeon HD 7990 6GB Video Card ($644.98 @ Newegg)
Case: NZXT Switch 810 (Black) ATX Full Tower Case ($136.00 @ Amazon)
Power Supply: XFX 750W 80 PLUS Bronze Certified ATX12V / EPS12V Power Supply ($97.99 @ Amazon)
Optical Drive: Lite-On iHAS124-04 DVD/CD Writer ($17.98 @ Outlet PC)
Operating System: Microsoft Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 (OEM) (64-bit) ($89.00 @ Amazon)
Total: $1400.13
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-10 01:16 EDT-0400)
or
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU: AMD Phenom II X6 1100T Black 3.3GHz 6-Core Processor ($192.14 @ NCIX US)
Motherboard: Asus M5A97 LE R2.0 ATX AM3+ Motherboard ($84.24 @ Amazon)
Memory: G.Skill Ripjaws X Series 8GB (2 x 4GB) DDR3-1866 Memory ($74.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Kingston SSDNow V300 Series 120GB 2.5" Solid State Disk ($84.99 @ NCIX US)
Storage: Seagate Barracuda 1TB 3.5" 7200RPM Internal Hard Drive ($59.97 @ SuperBiiz)
Video Card: PowerColor Radeon HD 7990 6GB Video Card ($644.98 @ Newegg)
Case: NZXT Switch 810 (Black) ATX Full Tower Case ($136.00 @ Amazon)
Power Supply: XFX 750W 80 PLUS Bronze Certified ATX12V / EPS12V Power Supply ($97.99 @ Amazon)
Optical Drive: Lite-On iHAS124-04 DVD/CD Writer ($17.98 @ Outlet PC)
Operating System: Microsoft Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 (OEM) (64-bit) ($89.00 @ Amazon)
Total: $1482.28
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-10 01:28 EDT-0400)
Note: I fixed this bottle-necking issue with only about $300-$400 (CPU upgrade and a motherboard upgrade since the CPU socket and motherboard socket needed to be the same) and since the Phenom II x4 is a quad core (Note: x4 = 4 cores) and the Phenom II x6 is a six-core (Note: x6 = 6 cores) these would be a lot more suitable for this setup.
Note About Sockets:
Note: Your sockets must match your motherboard and vice versa therefore this means that if you have an AMD Phenom x6 (6x = 6 cores) you would need a motherboard that has a AM3+ socket. So how do I tell which motherboard has which socket? It's actually quite easy and here's how to. Generally on a site like Newegg or Amazon the description will look like this (see below). There are a couple of things to look for in the name before you consider on buying it.
Example:
ASUS M5A97 LE R2.0 AM3+ AMD 970 SATA 6GB/s USB 3.0 ATX AMD Motherboard with UEFI BIOS
Complete Name Breakdown:
Brand Name: ASUS
Model: M5A97 LE R2.0
Motherboard Socket Type: AM3+ (AMD Socket)
Chipset: 970
Type of HDD/SSD Connection: SATA
HDD/SSD Max Transfer Speed: 6 GB/s
Maximum USB Speed Supported: USB 3.0
Motherboard Form Factor: ATX
Type of Motherboard: AMD Motherboard
BIOS: UEFI BIOS (If not listed it does not support UEFI Bios)
Special Features (To Look for when Upgrading a Motherboard):
[img=350x350]http://i1201.photobucket.com/albums/bb358/Derek_Bermel/AsusAMDMotherboardBios.jpg[/img]
UEFI BIOS: This is not like the old bios where everything is all controlled by a keyboard. This new and improved Bios system actually allows users to point and click with the mouse (and if needed use keyboard). This new and improved Bios makes over-clocking a computer really simple as well as changing Bios settings. I would recommend aiming for this as well when you upgrade your motherboard. The two motherboard companies I would recommend with this feature are ASUS and ASrock. Both of these companies are great motherboard companies and both companies usually support the UEFI BIOS.

USB 3.0: This is a nice little feature if you want your motherboard to be useful in the future this little feature has improved speed over USB 2.0 (Black USB port) by 10 times the speed. This is backwards compatible with USB 2.0 as well. These come off as blue USB ports on the front of the case. You want to look for the header on the motherboard (shown above).
AMD vs. Intel Definitions:
There are two main types of computer chips in this world. The first is Intel (Integrated Electronics) which is your maker of the Pentium & the I series micro processors (i3, i5, i7). They are currently the largest micro-processor manufacturer. The second major company is AMD (Advanced Microdigital Devices) which is the only other major competitor of Intel.
Upgrading Motherboards & Supported Processors:
Note: All Processors are linked to a Wikipedia specified page (if available) in order to better explain and answer any in depth questions you may have.
Socket 0 - Pin Count: 168:
Intel: 80486 DX
Socket 1 - Pin Count: 169:
Intel: 80486 DX
Intel: 80486 DX2
Intel: 80486 SX
Intel: 80486 SX2
Socket 2 - Pin Count: 238:
Intel: 80486 DX
Intel: 80486 DX2
Intel: 80486 SX
Intel: 80486 SX2
Intel: Pentium Overdrive
Socket 3 - Pin Count 237:
Intel: 80486 DX
Intel: 80486 DX2
Intel: 80486 DX 4
Intel: 80486 SX
Intel: 80486 SX2
Intel: Pentium Overdrive
AMD: 5x86
Socket 4 - Pin Count: 273:
Intel: Pentium-60
Intel: Pentium-66
Socket 5 - Pin Count: 320:
Intel: Pentium 75 thru Pentium 120
AMD: K5
IDT: WinChip C6
IDT: WinChip C2
Socket 6 - Pin Count: 235:
Intel: 80486 DX
Intel: 80486 DX2
Intel: 80486 DX4
Intel: 80486 SX
Intel: 80486 SX2
Intel: Pentium Overdrive
AMD: 5x86
Socket 7 - Pin Count: 321:
Intel: Pentium 75 thru Pentium 200
Intel: Pentium MMX
AMD: K5
AMD: K6
Cyrix: 6x86
Cyrix: 6x86MX
Cyrix: MII
Socket Super 7 - Pin Count: 321:
AMD: K6-2
AMD: K6-III
Rise: mP6
Cyrix: MII
Socket 8 - Pin Count: 387:
Intel: Pertium Pro
Slot 1 (SC242) - Pin Count: 242:
Intel: Pentium II
Intel: Pentium III (Cartridge)
Intel: Celeron SEPP (Cartridge)
Slot 2 - Pin Count: 330:
Intel: Pentium II Xeon
Socket 463 (Socket NexGen) - Pin Count: 463:
NexGen: Nx586
Socket 587 - Pin Count: 587:
Aplha: 21164A
Slot A - Pin Count: 242:
AMD: Athlon
Slot B - Pin Count: 587:
Alpha: 21264
Socket 370 - Pin Count: 370:
Intel: Pentium III (FC-PGA)
Intel: Celeron
VIA: Cyrix III
VIA: C3
Socket 462 (Socket A) - Pin Count: 462:
AMD: Athlon
AMD: Duron
AMD: Athlon XP
AMD: Athlon XP-M
AMD: Athlon MP
AMD: Sempron
Socket 423 (PGA423) - Pin Count: 423:
Intel: Pentium 4
Socket 478 (Socket N) - Pin Count: 478:
Intel: Pentium 4
Intel: Celeron
Intel: Pentium 4 EE (Extreme Edition)
Intel: Pentium 4 M (Mobile Processor - Laptops)
Socket 495 - Pin Count: 495:
Intel: Celeron
Intel: Pentium 3
PAC418 - Pin Count: 418:
Intel: Itanium
Socket 603 - Pin Count: 603:
Intel: Xeon
PAC611 - Pin Count: 611:
Intel: Itanium 2
HP: PA-8800
HP: PA-8900
Socket 604 - Pin Count: 604:
Intel: Xeon
Socket 754 - Pin Count: 754:
AMD: Athlon 64
AMD: Sempron
AMD: Turion 64
Socket 940 - Pin Count: 940:
AMD: Opteron
AMD: Athlon 64 FX
Socket 479 - Pin Count: 479:
Intel: Pentium M
Intel: Celeron M
Socket 939 - Pin Count: 939:
AMD: Athlon 64
AMD: Athlon 64 FX
AMD: Athlon 64 X2 (Dual Core)
AMD: Opteron
LGA 775 (Socket T) - Pin Count: 775:
Intel: Pentium 4
Intel: Pentium D
Intel: Celeron
Intel: Celeron D
Intel: Pentium XE (Extreme Edition)
Intel: Core 2 Duo (2 Cores)
Intel: Core 2 Quad (4 Cores)
Intel: Xeon
Socket 563 - Pin Count: 563:
AMD: Athlon XP-M
Socket M - Pin Count: 478:
Intel: Core Solo
Intel: Core Duo
Intel: Dual-Core Xeon
Intel: Core 2 Duo
LGA 771 (Socket J) - Pin Count: 771:
Intel: Xeon
Socket S1 - Pin Count: 638:
AMD: Turion 64 x2
Socket AM2 - Pin Count: 940:
AMD: Athlon 64
AMD: Athlon 64 x2
Socket F/Socket L (Socket 1207FX) - Pin Count: 1,207:
AMD: Athlon 64 FX (Socket L Support Only)
AMD: Opteron
Socket AM2+ - Pin Count: 940:
AMD: Athlon 64
AMD: Athlon x2
AMD: Phenom
AMD: Phenom II
Socket P - Pin Count: 478:
Intel: Core 2
Socket 441 - Pin Count: 441:
Intel: Atom
LGA 1366 (Socket B) - Pin Count: 1,366:
Intel: Core i7 (900 Series)
Intel: Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series)
rPGA 988A (Socket G1) - Pin Count: 988:
Intel: Core i7 (600, 700, 800, 900 Series)
Intel: Core i5 (400, 500 Series)
Intel: Core i3 (300 Series)
Intel: Pentium (P6000 Series)
Intel: Celeron (P4000 Series)
Socket AM3 - Pin Count: 940/941 (Depending):
AMD: Pheonom II
AMD: Athlon II
AMD: Sempron
LGA 1156 (Socket H) - Pin Count: 1,156:
Intel: Core i7 (800 Series)
Intel: Core i5 (600, 700 Series)
Intel: Core i3 (500 Series)
Intel: Xeon (X3400, L3400 Series)
Intel: Pentium (G6000 Series)
Intel: Celeron (G1000 Series)
Socket G34 - Pin Count: 1,974:
AMD: Opteron (6000 Series)
Socket C32 - Pin Count: 1,207:
AMD: Opteron (4000 Series)
LGA 1248 - Pin Count: 1,248:
Intel: Itanium (9300 Series)
LGA 1567 - Pin Count: 1,567:
Intel: Xeon (6500, 7500 Series)
LGA 1155 (Socket H2) - Pin Count: 1,155:
Intel: Sandy Bridge
Intel: Ivy Bridge
LGA 2011 (Socket R) - Pin Count: 2,011:
Intel: Sandy Bridge-E
Intel: Ivy Bridge-E
rPGA 988B (Socket G2) - Pin Count: 988:
Intel: Core i7 (2000, 3000 series)
Intel: Core i5 (2000, 3000 series)
Intel: Core i3 (2000, 3000 series)
Socket FM1 - Pin Count: 905:
AMD: Llano Processors
AM3+ - Pin Count: 942 (CPU Pin Count: 71):
AMD: FX Vishera
AMD: FX Zambezi
AMD: Pheonom II
AMD: Athlon II
AMD: Sempron
Socket FM2 - Pin Count: 904:
AMD: Trinity Processors
LGA 1150 (Socket H3) - Pin Count: 1,150:
Intel: Haswell Processors (Desktop)
Intel: Broadwell Processors (Desktop)
Socket G3 - Pin Count: 889:
Intel: Haswell Processors (Notebook)
Intel: Broadwell Processors (Notebook)
End of Processor & Motherboard Socket List
Note: If your CPU processor that you want to upgrade to does not match the motherboard socket listed above, then you will need to upgrade your motherboard along with your CPU at the same time.
Overclocking:
There is a couple of Overclocking things I would like to talk about with you since this is dealing with new built computers as well as upgrading an existing computers. This section will explain some helpful tips on motherboards, CPU's and cooling for overclocking.
What To Look For When Planning To Overclock:
[img=350x350]http://i1201.photobucket.com/albums/bb358/Derek_Bermel/sabertooth-990fx-r2.jpg[/img]
Note: Notice that the heat sinks are connected by tubing to allow heat to transfer between the two heat exchanges. This allows better heat dissipation between the two heat exchanges, thus keeping your motherboard much cooler. Also notice that the south bridge (where the ASUS logo normally is) has a cover with vents over it, this also acts like a heat exchange. This particular motherboard is an ASUS Sabertooth 990FX r2.0 (AMD Motherboard).
[img=350x350]http://i1201.photobucket.com/albums/bb358/Derek_Bermel/AsusAMDMotherboardBios.jpg[/img]
Also another nice this is the UEFI Bios (which is shown above) and this is an easier interference to work with when overclocking your system. This Bios version features an interactive mouse and keyboard vs. the older style which only had an interference of a keyboard. This is shown above on the main screen and an in depth demo of the features can be found by clicking here. Also this would benefit your experience as it a lot easier to overclock your CPU.
Cooling Your CPU Processor:
This is probably the most critical thing on this page all together simply because if you do not have proper cooling your CPU will shut down from overheating (much like a car will shut off when it overheats), at which point you have a risk of running your CPU. There are a variety of ways to cool down your CPU even in the most extreme conditions. These methods include 3 main ways: air cooling, water cooling with a closed loop system, and finally water cooling with a custom made system. I am going to go into depth on some of the more common air coolers and water coolers with closed loop systems out there. I will not be talking about custom water cooler loops in this article, however I will link a page where you can learn about that as well.
Air Coolers:
Air Cooling Definitions:
CFM (Cubic Feet Per Minute): The higher this is the better the air cooler will be. This number refers to the amount of air that the fan moves.
dbA (Decibel): The lower this number the better. This number is in reference to the noise level of the fans spinning.


Cool Master EVO 212: (both pictures above) is a perfect example of a good air cooler. Notice: The heat pipes on the bottom of the unit to help the transfer of heat, this is a really effective method. This keeps the processor from getting too hot as the heat is transferred into the heat pipes then blown out thru the fans.
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU Cooler: Cooler Master Hyper 212 EVO 82.9 CFM Sleeve Bearing CPU Cooler ($29.99 @ Microcenter)
Total: $29.99
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-10 07:00 EDT-0400)


Noctua NH-U9B SE2: This is another great cooler, also a lot less noisy than the Cool Master EVO 212 (with stock fans). Notice: The heat pipes on this air cooler are very similar to the heat pipes on the Cool Master Evo 212, and that the air gets transferred through the heat pipes and pushed out the back exhaust while the front fan brings cold air into the system.
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU Cooler: Noctua NH-U9B SE2 37.9 CFM CPU Cooler ($51.15 @ Amazon)
Total: $51.15
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-10 06:59 EDT-0400)
Notice: Air coolers cool greatly and while I have absolutely nothing against them, they do put a lot of stress on the motherboard. Notice how all of these air coolers are held in by four screws depending on the socket type? Imagine your motherboard having to support that weight holding it out over air. Not to mention it blocks air flow in your case. They are good for what they do and are on the cheaper side of things, however they do have some drawbacks that come along with them. You will see what I mean in the next section.
Water Cooling (Closed Loop) - Corsair Section:
Note: Water coolers are divided into two separate classifications, closed loop and custom loop. The closed loop water coolers are the pre-made water coolers that you can buy from your local PC part store. These are usually less effective than the custom water coolers, but still are classified for medium to heavy overclocking. They are measured buy the size of the radiator and the size of the fan in your case. For example if you can fit two 120 mm fans in the top of your case (above the motherboard) then you would call this a 240 mm Rad (Radiator). Same thing if you can only fit one 140 mm fan in the back of your case, this would be called a 140 mm Rad (Radiator).
That being said there are a few choice selections that we will cover in this guide today:
H80i (Single 120 mm Radiator):

What the Corsair H80i looks like assembled.

The H80i installed in a case, with a push/pull configuration.
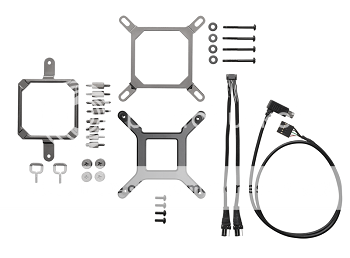
The included hardware that comes in the package with the H80i
Description:
Let me take a minute to explain how they work. You have 2 retention rings, (as shown in the bottom picture, the two big square pieces) a Corsair Link and USB 2.0 header cable, (which allows you to control the water cooler through a desktop program), and your various bolts and pieces. For an in depth guide on how to install it please click here (Also shows the H100i as well). This H80i uses two 120 mm fans in a push pull configuration (see above for push/pull configuration) and a CPU block that connects to the CPU Processor chip and keeps it cool. Because it is a single 120 mm radiator (uses two 120 mm fans) it allows it to be installed in virtually any case (so long as you don't have a 140 mm case only). The H80i also comes with pre-applied thermal compound (no need to apply it yourself).
Specifications (Breakdown):
Socket Compatibility (Motherboard & CPU):
Intel: LGA 1150; LGA 1155; LGA 1156; LGA 1366; LGA 2011
AMD: AM2; AM3; AM3+; FM1; FM2
Noise Level (dbA):
37.7 (Kind of noisy but could be worse, my suggestion would be to get some quieter fans).
Fan Air Flow (CFM):
77 CFM (Really good Air Flow for a single fan)
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU Cooler: Corsair H80i 77.0 CFM Liquid CPU Cooler ($79.99 @ Amazon)
Total: $79.99
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-11 00:59 EDT-0400)
H90 (Single 140 mm Radiator):

What the Corsair H90 looks like assembled

The Corsair H90 installed with a "push" configuration (Add another fan to make the push/pull configuration)

The Hardware included in the H90 package
Description:
So this one differs a little bit from the H80i. Instead of using 120 mm fans they use 140 mm fans, which spin slower to move the same air as a 120 mm, therefore creating less noise and better performance (since it has a bigger surface area). Most of the newer cases support 140 mm rear exhaust fans. For an in depth video on the features and benefits, as well as how to install the Corsair H90, please click here.
Specifications (Breakdown):
Socket Compatibility (Motherboard & CPU):
Intel: LGA 1155; LGA 1156; LGA 1366; LGA 2011
AMD: AM2; AM3; AM3+; FM1; FM2
Noise Level (dbA):
35 (About 2 dbA less then the H80i)
Fan Air Flow (CFM):
94 CFM (Almost a 20 CFM difference between the H80i & the H90)
PCPartPicker part list / Price breakdown by merchant / Benchmarks
CPU Cooler: Corsair H90 94.0 CFM Liquid CPU Cooler ($84.99 @ Newegg)
Total: $84.99
(Prices include shipping, taxes, and discounts when available.)
(Generated by PCPartPicker 2013-10-11 01:55 EDT-0400)
Upgrading Your Graphics Card[/u][/b]
This section will not have as much reading as the last one. In this section we will be talking about how to upgrade your graphics card. It will explain what to look for in new graphics cards and give a few examples on how to go about doing so, making sure that you get the best deal for the price. This can be especially helpful since it took me awhile to learn about graphics cards.


