Common Monitor Terminology
Color Depth : The color depth of an LCD determines the number of colors that the primary colors can render.
Inputs : The four most common monitor inputs are as follows:
HDMI:

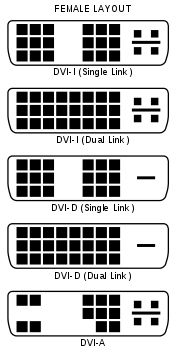
DVI:
There are multiple formats for DVI. The newer 2560 x 1440 and 2560 x 1080 formats require the DVI D-Link.
These are the different types:
D-Link: Dual Link
S-Link: Single Link
A-Link: Analog Link
VGA (commonly found on low end graphics cards, most laptops alongside HDMI output, and older PCs manufactured before 2008) :

Display Port (commonly found on most Macbooks, professional grade GPUs like ATI Fire Pro and NVIDIA K4000, and higher end monitors) :

The Resolution : A pixel is a small square of color and the resolution tells you how many pixels an image has. The more pixels, the smoother and less jagged an image you have. Think Mario from the original Super Mario Brothers, then him in modern games. That visual difference is because there are more pixels used to construct his image.
Note: How "jagged" the screen appears to be does depend on its size of the monitor and your distance from it. See "Size" section below for explanation.
The resolution of an image is represented as “Horizontal Pixels X Vertical Pixels”. So a resolution of 1920x1080 is 1920 pixels wide, by 1080 pixels tall.
There a few shorthand ways of specifying a rough resolution.
Most common resolutions:
- WXGA: 1440 x 900 (15" - 19" display - most common for USB monitors and small displays)
- UXGA: 1600 x 1200 (17" - 21" display, most common for $100 - $150 displays)
- HDTV: 1920 x 1080 (standard 22" - 27" display, also standard HDTV format, less common on smaller displays)
- WUXGA: 1920 x 1200 (commonly found on smaller high resolution screens such as Google Nexus 7, HTC One)
- QHD: 2560 x 1440 (commonly found on 27" - 30" IPS monitors manufactured in Korea, ideal for gaming, large spreadsheets, and Photoshop / Adobe CS 5/6 )
- WQXGA: 2560 x 1600 (standard large format - ideal for Photoshop and CAD, high end gaming)
- WFHD: 2560 x 1080 (standard ultra wide format - ideal for movie watching, strategy games, and Photoshop and rendering)
- WQUXGA: 3840 x 2400 (this is the ultra high end new format being referred to in media as 4K)
As your resolution increases, so does the demands on whatever is pushing your graphics. The GPU has to calculate what each pixel is doing every given frame. At 720p, that means its dealing with roughly a million pixels, go up to 1080p and its suddenly pushing two million pixels.
Your performance wont drop by a half because its got double the pixels to deal with, but it will make a difference.
HDCP : This stands for "High Definition Copy Protection". If you plan to buy a monitor with the idea of movie watching in mind, and your monitor is not HDCP compliant, you will not be able to watch movies from your PC.
Aspect Ratio : The aspect ratio is the proportional dimension between an image's width and height. The wider an image it is, the less likely it will have black bars around the image. The most common aspect ratios are 4:3 (standard television format), 16:9 (standard wide format), and 1.85:1 (standard cinema format), and 2.35:1 (or 21:9, standard ultra wide cinema format).
Contrast Ratio : This is the most hotly debated topic among monitor enthusiasts because a lot of manufacturers distort what this actually is. In layman's terms it is the difference between the brightest resolution your monitor can make and the darkest.
Resolution : This is how many pixels are in a standard inch on a monitor. The more pixels you are able to get out of an inch, the sharper your image will be.
Response Time : This is how long it takes for a monitor pixel to change from one color to the next. The longer the time, the longer it takes to redraw.
Refresh Rate : This is how fast the panel can change to a different image, literally how fast the monitor can display new frames. It is measured in Hz (Times per Second). It’s hard to explain, but a higher refresh rate leads to everything just generally being smoother, as more images are coming from the monitor with less of a delay between each one. Most monitors run at a refresh rate of 60hz, with some TN panels running at 120Hz or above in some cases.
Korean 1440p IPS monitors, on the cheap
Currently on the market there are a range of IPS 1440p screens, typically starting at ~$600 and going upward depending on physical size, build quality, brand, exact type of IPS panel being used, etc from your typical retailers.
However, as of the time of writing, there is an alternative to these mainstream options. Various Korean manufacturers (QNIX, Yamakasi, CROSSOVER) and re-sellers are offering IPS panel 1440p monitors quite cheaply through Ebay, for example a Yamakasi Catleap Q270 SE (not the monitor mentioned in the "Overclocking section") 1440p IPS monitor can be had for about $350-400.
The majority of these panels are rejected Apple stock, they were originally intended to be used in Apple iMac's or Apple Cinema displays but were for one reason or another ended up not being up to par with Apple standards. These leftover panels are sold to the various manufacturers who create the monitors that are available on Ebay now.
The panels are A- grade, meaning they are more likely to have dead pixels and other defects than the A+ grade panels that make their way into Apple displays. Resellers of these monitors often offer a "Pixel Perfect" option, where for $30-40 more you can be guaranteed a monitor without any dead pixels.[/b]
The refresh rate also impacts on a monitors ability to show 3D content. For more info, check the "3D" section below.
Types Of Monitor Panels
IPS : Stands for "In Plane Switching". This type of LCD panel is known for excellent color switching and viewing angles. Considered to be the most expensive to manufacture, found on most newer PC LCDs, and higher end HDTVs from Samsung, Sony, LG, Vizio, etc.
PVA : Stands for "Patterned Vertical Alignment". Known for high contrast ratios, higher end black levels, and viewing alignment. Sluggish pixel response time compared to IPS and TN, found on professional level displays and is more expensive to manufacture.
TN : Stands for "Twisted Nematic". The most common type of panel found on desktop monitors. Relatively inexpensive to manufacture. Has fast pixel response time, but known for lackluster grey scale quality and mediocre color spectrum.
If You Are Interested In Buying A Monitor Please Fill Out The Following As This Will Help Narrow Down Recommended Choices:
1. What Is Your Country Of Origin?
2. What do you plan to do with this monitor? (ex. Games, Movie Watching, Photo Editing, etc.)
3. What resolution and screen size do you want?
4. What refresh rate do you want? (ex. 60 hz , 70 hz.)
5. How much are you looking to spend?
6. Brands Preferred (ex. Samsung, Acer, Asus, AOC, HP, Viewsonic, etc. )
7. Brands Not Preferred (state reason why)
8. Are You Buying More Than One Monitor?
9. How Many Displays Can Your GPU Support Maximum? And what GPU and driver version are you using if applicable?
10. What Port Do You Want To Connect To (ex. DVI-D, HDMI, etc).
11. Is This Monitor A Primary Display Or A Secondary Display?
12. Is This A Secondary Display For A Laptop?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CREDIT GOES TO Manofchalk as some of the information in this thread was pulled from his monitor guide: http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/id-1661174/parts-guide-monitors.html
Color Depth : The color depth of an LCD determines the number of colors that the primary colors can render.
Inputs : The four most common monitor inputs are as follows:
HDMI:

DVI:
There are multiple formats for DVI. The newer 2560 x 1440 and 2560 x 1080 formats require the DVI D-Link.
These are the different types:
D-Link: Dual Link
S-Link: Single Link
A-Link: Analog Link

VGA (commonly found on low end graphics cards, most laptops alongside HDMI output, and older PCs manufactured before 2008) :

Display Port (commonly found on most Macbooks, professional grade GPUs like ATI Fire Pro and NVIDIA K4000, and higher end monitors) :

The Resolution : A pixel is a small square of color and the resolution tells you how many pixels an image has. The more pixels, the smoother and less jagged an image you have. Think Mario from the original Super Mario Brothers, then him in modern games. That visual difference is because there are more pixels used to construct his image.
Note: How "jagged" the screen appears to be does depend on its size of the monitor and your distance from it. See "Size" section below for explanation.
The resolution of an image is represented as “Horizontal Pixels X Vertical Pixels”. So a resolution of 1920x1080 is 1920 pixels wide, by 1080 pixels tall.
There a few shorthand ways of specifying a rough resolution.
Most common resolutions:
- WXGA: 1440 x 900 (15" - 19" display - most common for USB monitors and small displays)
- UXGA: 1600 x 1200 (17" - 21" display, most common for $100 - $150 displays)
- HDTV: 1920 x 1080 (standard 22" - 27" display, also standard HDTV format, less common on smaller displays)
- WUXGA: 1920 x 1200 (commonly found on smaller high resolution screens such as Google Nexus 7, HTC One)
- QHD: 2560 x 1440 (commonly found on 27" - 30" IPS monitors manufactured in Korea, ideal for gaming, large spreadsheets, and Photoshop / Adobe CS 5/6 )
- WQXGA: 2560 x 1600 (standard large format - ideal for Photoshop and CAD, high end gaming)
- WFHD: 2560 x 1080 (standard ultra wide format - ideal for movie watching, strategy games, and Photoshop and rendering)
- WQUXGA: 3840 x 2400 (this is the ultra high end new format being referred to in media as 4K)
As your resolution increases, so does the demands on whatever is pushing your graphics. The GPU has to calculate what each pixel is doing every given frame. At 720p, that means its dealing with roughly a million pixels, go up to 1080p and its suddenly pushing two million pixels.
Your performance wont drop by a half because its got double the pixels to deal with, but it will make a difference.
HDCP : This stands for "High Definition Copy Protection". If you plan to buy a monitor with the idea of movie watching in mind, and your monitor is not HDCP compliant, you will not be able to watch movies from your PC.
Aspect Ratio : The aspect ratio is the proportional dimension between an image's width and height. The wider an image it is, the less likely it will have black bars around the image. The most common aspect ratios are 4:3 (standard television format), 16:9 (standard wide format), and 1.85:1 (standard cinema format), and 2.35:1 (or 21:9, standard ultra wide cinema format).
Contrast Ratio : This is the most hotly debated topic among monitor enthusiasts because a lot of manufacturers distort what this actually is. In layman's terms it is the difference between the brightest resolution your monitor can make and the darkest.
Resolution : This is how many pixels are in a standard inch on a monitor. The more pixels you are able to get out of an inch, the sharper your image will be.
Response Time : This is how long it takes for a monitor pixel to change from one color to the next. The longer the time, the longer it takes to redraw.
Refresh Rate : This is how fast the panel can change to a different image, literally how fast the monitor can display new frames. It is measured in Hz (Times per Second). It’s hard to explain, but a higher refresh rate leads to everything just generally being smoother, as more images are coming from the monitor with less of a delay between each one. Most monitors run at a refresh rate of 60hz, with some TN panels running at 120Hz or above in some cases.
Korean 1440p IPS monitors, on the cheap
Currently on the market there are a range of IPS 1440p screens, typically starting at ~$600 and going upward depending on physical size, build quality, brand, exact type of IPS panel being used, etc from your typical retailers.
However, as of the time of writing, there is an alternative to these mainstream options. Various Korean manufacturers (QNIX, Yamakasi, CROSSOVER) and re-sellers are offering IPS panel 1440p monitors quite cheaply through Ebay, for example a Yamakasi Catleap Q270 SE (not the monitor mentioned in the "Overclocking section") 1440p IPS monitor can be had for about $350-400.
The majority of these panels are rejected Apple stock, they were originally intended to be used in Apple iMac's or Apple Cinema displays but were for one reason or another ended up not being up to par with Apple standards. These leftover panels are sold to the various manufacturers who create the monitors that are available on Ebay now.
The panels are A- grade, meaning they are more likely to have dead pixels and other defects than the A+ grade panels that make their way into Apple displays. Resellers of these monitors often offer a "Pixel Perfect" option, where for $30-40 more you can be guaranteed a monitor without any dead pixels.[/b]
The refresh rate also impacts on a monitors ability to show 3D content. For more info, check the "3D" section below.
Types Of Monitor Panels
IPS : Stands for "In Plane Switching". This type of LCD panel is known for excellent color switching and viewing angles. Considered to be the most expensive to manufacture, found on most newer PC LCDs, and higher end HDTVs from Samsung, Sony, LG, Vizio, etc.
PVA : Stands for "Patterned Vertical Alignment". Known for high contrast ratios, higher end black levels, and viewing alignment. Sluggish pixel response time compared to IPS and TN, found on professional level displays and is more expensive to manufacture.
TN : Stands for "Twisted Nematic". The most common type of panel found on desktop monitors. Relatively inexpensive to manufacture. Has fast pixel response time, but known for lackluster grey scale quality and mediocre color spectrum.
If You Are Interested In Buying A Monitor Please Fill Out The Following As This Will Help Narrow Down Recommended Choices:
1. What Is Your Country Of Origin?
2. What do you plan to do with this monitor? (ex. Games, Movie Watching, Photo Editing, etc.)
3. What resolution and screen size do you want?
4. What refresh rate do you want? (ex. 60 hz , 70 hz.)
5. How much are you looking to spend?
6. Brands Preferred (ex. Samsung, Acer, Asus, AOC, HP, Viewsonic, etc. )
7. Brands Not Preferred (state reason why)
8. Are You Buying More Than One Monitor?
9. How Many Displays Can Your GPU Support Maximum? And what GPU and driver version are you using if applicable?
10. What Port Do You Want To Connect To (ex. DVI-D, HDMI, etc).
11. Is This Monitor A Primary Display Or A Secondary Display?
12. Is This A Secondary Display For A Laptop?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CREDIT GOES TO Manofchalk as some of the information in this thread was pulled from his monitor guide: http://www.tomshardware.com/forum/id-1661174/parts-guide-monitors.html

